Closing the gap in future vehicle development
How IoT technology will change the test culture
Cost-efficient solutions are a key factor in ensuring competitiveness in the development of future software-based vehicle functions. Due to the disproportionate increase in complexity, their validation and quality assurance is a high priority. In addition, the Corona pandemic shows how fragile current development processes are when local access to vehicle data is not possible. The use of IoT technologies can support the traditional development process and help in the transition to the software-defined vehicle. At the same time, the connection of cloud platforms provides cross-departmental access to test data, which also strengthens cross-domain holistic development, demonstrates synergies, and provides the basis for a sustainable value chain.
The approach presented here divides the phases of validation in terms of test equipment accessibility: local on site, conditional access, inaccessible.
Phase 1 | Local on site

IoT-enabled measurement equipment is installed to complement conventional measurement technology in the first phase. In addition to the vehicle status, this phase documents the functionality of all measurement equipment. Contextual information is thus added. If gateway functionalities are already activated at this stage, extended functions of conventional measurement technology, such as software updates, can also be used and additional added value can be created.
Phase 2 | Conditional access
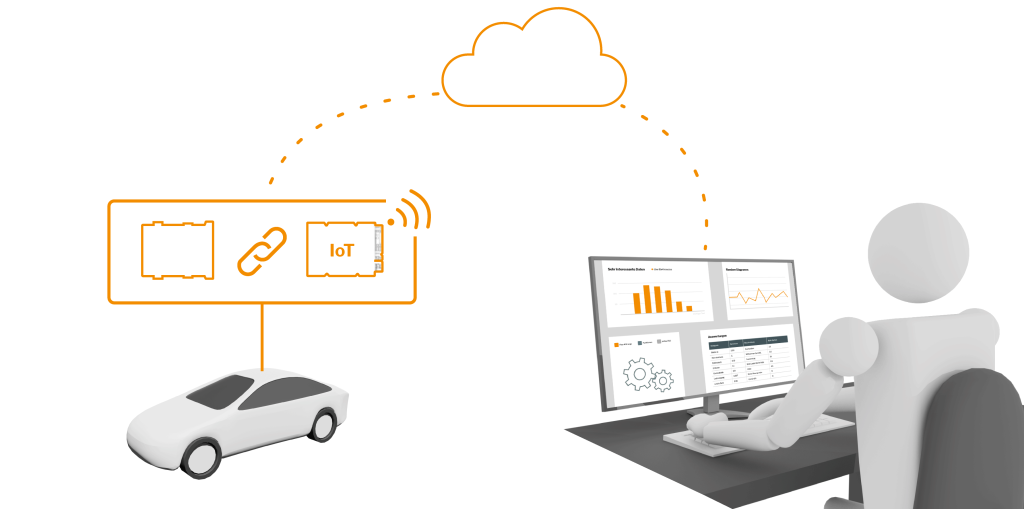
In the next phase, the scope is extended by shifting the vehicle data acquisition from conventional to IoT-enabled measuring devices, thus freeing up existing resources. As accessibility changes, the need for management will increase. To ensure comparability of data, the scope or selection of data is of particular importance, as is the way in which this data is collected and stored. The shift in data collection also goes hand in hand with cyber security compliance issues.
Phase 3 | Remote access
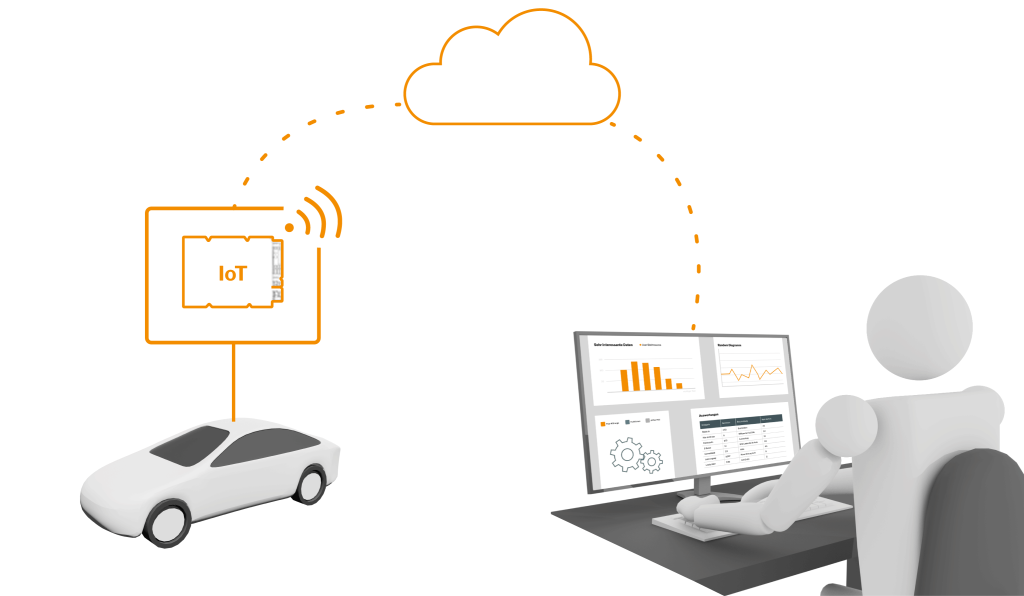
In the third phase, as new features mature, the amount of vehicle data can be reduced to enable testing in the field with current mobile technologies. Evolving mobile standards and reduced latency pave the way for additional testing of intelligent vehicle-cloud interactions to offload computationally intensive and latency sensitive functions. This represents a bridging technology to the software-defined vehicle, enabling the use of cloud-vehicle loops and various downstream processing chains for efficient use of collected vehicle data.



